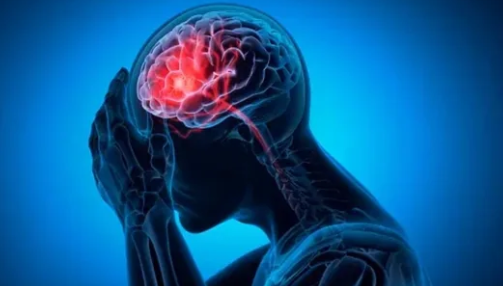
The medical community is sounding the alarm on a crucial connection between sepsis and stroke, two severe and life-threatening conditions. Sepsis, a systemic infection that triggers widespread inflammation, has long been recognized for its devastating effects on multiple organs. Now, studies show a significant link between sepsis and an increased risk of stroke, even after the infection has been treated.
When the body experiences sepsis, the immune system goes into overdrive, leading to blood clot formation, which can obstruct arteries and result in a stroke. The inflammation from sepsis can also weaken blood vessels, making them more prone to rupture. This heightened stroke risk can persist for months after recovery, making post-sepsis care critical.
Understanding this connection is vital as stroke is a leading cause of disability and death worldwide. Those who have experienced sepsis are urged to remain vigilant about their neurological health, as the risk of stroke does not vanish with the resolution of the infection.
Early detection and treatment of infections can prevent the onset of sepsis. For those recovering from sepsis, managing inflammation and controlling underlying risk factors like high blood pressure and diabetes are essential. Regular medical check-ups, lifestyle changes, and a healthy diet can further mitigate stroke risk, particularly in post-sepsis patients.
As research continues to unravel the complex relationship between sepsis and stroke, healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of public awareness. Prompt treatment, patient education, and lifestyle adjustments are the pillars of prevention, ensuring that both sepsis and stroke risks are minimized.








 India
India