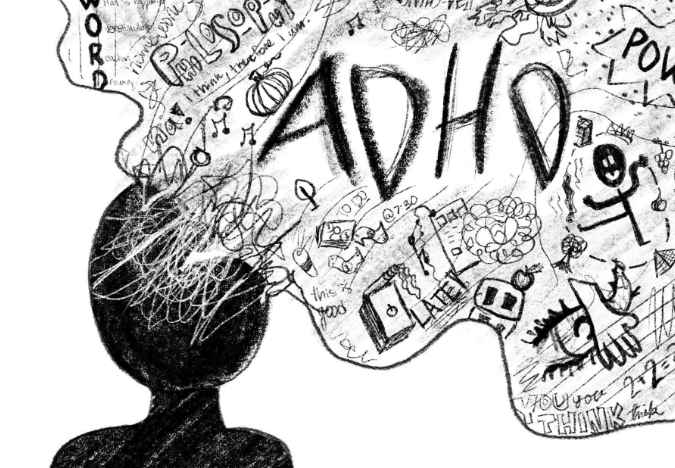
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects millions of people worldwide, manifesting in symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. While the exact causes of ADHD are not fully understood, experts believe a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors play significant roles in influencing the severity and expression of symptoms.
Dr. Anjali Mehta, a renowned therapist specializing in ADHD, sheds light on the various factors that can impact the symptoms of this condition, offering insights into effective management strategies.
Genetic Factors: “Genetics are a major contributing factor in ADHD,” explains Dr. Mehta. “Research shows that ADHD can run in families, indicating a hereditary component. If a parent or sibling has ADHD, there is a higher likelihood that another family member may also have it.”
Environmental Factors: Environmental influences, particularly during pregnancy and early childhood, can affect the development of ADHD. “Exposure to toxins such as lead, alcohol, or tobacco smoke during pregnancy, premature birth, and low birth weight are some risk factors,” Dr. Mehta notes. “Additionally, a chaotic or stressful home environment can exacerbate ADHD symptoms.”
Diet and Nutrition: While diet alone does not cause ADHD, certain dietary choices can influence symptom severity. “A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports overall brain health,” says Dr. Mehta. “Conversely, excessive sugar, artificial additives, and food sensitivities may worsen symptoms in some individuals.”
Sleep Patterns: Adequate sleep is crucial for managing ADHD symptoms. “Sleep deprivation can lead to increased hyperactivity and inattention,” Dr. Mehta emphasizes. “Establishing a consistent sleep routine and ensuring sufficient rest can significantly improve symptom management.”
Physical Activity: Regular physical activity has been shown to help reduce ADHD symptoms. “Exercise increases the production of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which play key roles in attention and behavior regulation,” explains Dr. Mehta. “Encouraging daily physical activity can have a positive impact on symptom control.”
Therapeutic Interventions: Various therapeutic approaches, including behavioral therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and mindfulness practices, can help individuals manage ADHD symptoms. “Therapy provides strategies to improve focus, reduce impulsivity, and enhance organizational skills,” Dr. Mehta explains.
Medication: For many individuals, medication is an essential component of ADHD management. “Stimulant and non-stimulant medications can help regulate brain activity and improve attention and behavior,” says Dr. Mehta. “It’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the most effective medication and dosage.”
Support Systems: A strong support system, including family, friends, and educators, plays a vital role in managing ADHD. “Understanding and support from those around the individual can help reduce stress and improve coping strategies,” Dr. Mehta emphasizes.
In conclusion, managing ADHD requires a comprehensive approach that considers the interplay of various factors. By addressing genetic predispositions, optimizing the environment, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and utilizing therapeutic interventions, individuals with ADHD can lead fulfilling and productive lives.








 India
India